Table of contents
Docker-Volume
Docker allows mounting the filesystems as a volume to the containers. These volumes preserve all the data of the container and the data is persisted even if the container is deleted.
The default path is /var/lib/docker/volumes/ on Linux.
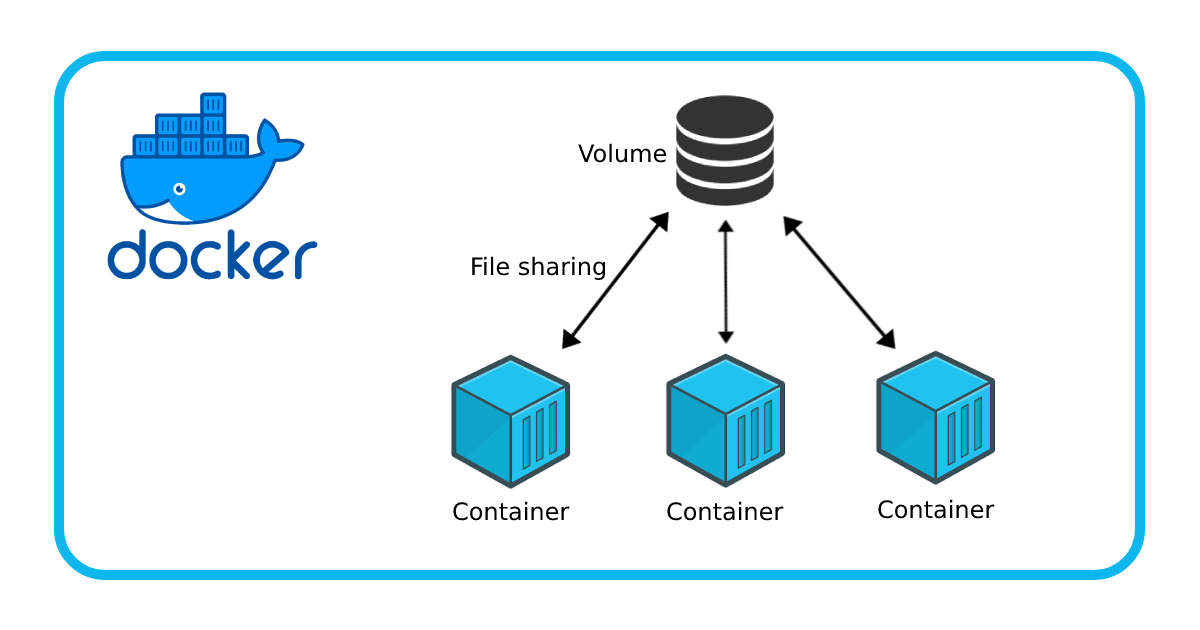
A volume can be mounted to multiple containers and it lies even if all containers are down. It can be removed only manually by the user.
Creating a Docker Volume
$docker volume create [volume_name]Listing a Docker Volume
$docker volume listMounting a volume.
docker run --mount source=[volume_name],destination=[path_in_container] [docker_image]Removing a Volume.
$docker volume rm [volume_name]Deleting all volumes at once.
$docker volume prune
Docker-Network
With Docker-Compose we create multiple containers, in that process, a space is created by Docker where those containers can communicate with each other and the host system. That space is known as Docker Network.
$docker network COMMAND
The COMMAND can be connected, create, disconnect, inspect, ls, prune, and rm.
Task - 1
Create a multi-container docker-compose file which will bring UP and bring DOWN containers in a single shot.
Use the
docker-compose upcommand with the-dflag to start a multi-container application in detached mode.
Use the
docker-compose scalecommand to increase or decrease the number of replicas for a specific service. You can also addreplicasin deployment file for auto-scaling.

Use the
docker-compose pscommand to view the status of all containers, anddocker-compose logsto view the logs of a specific service.
Use the
docker-compose downcommand to stop and remove all containers, networks, and volumes associated with the application
Task-2
Learn how to use Docker Volumes and Named Volumes to share files and directories between multiple containers.

Use the below command to create a volume.
$ docker volume create --name django-volume-final --opt device=/home/ubuntu/devops/volume/django-volume --opt o=bind --opt type=none django-volume-final


Create two or more containers that read and write data to the same volume using the
docker run --mountcommand.$ docker run -d --name django-notes-app -p 3000:3000 --mount source=django-volume-final,target=/app django-app:v1


Verify that the data is the same in all containers by using the docker exec command to run commands inside each container.
$ docker exec -it django-notes-app-V2 /bin/sh

Use the docker volume ls command to list all volumes and docker volume rm command to remove the volume when you're done.


Thanks for reading my article. Have a nice day.
You can follow me on LinkedIn for my daily updates:- linkedin.com/in/bandan-kumar-sahoo-131412203
